Car Safety Seat (Child)
Car seat positions
Using the right car seat can often prevent injuries to children during car accidents. As children grow, the type of car seat they need will change. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) have guidelines to help you find the right car seat for your child. Also look at the car seat owner’s manual.
Car seats are either rear-facing or forward-facing. As a rule, children should face the rear of the vehicle for as long as possible. This is the safest position for a child in a car crash. Use these recommendations:
|
Age
|
What to use
|
|
Birth to 1 year old
|
Always use a rear-facing car seat that's secured in the back seat.
|
|
1 to 3 years old
|
Babies and toddlers should ride in the back seat in a rear-facing car safety seat for as long as possible. That means until they reach the top weight or height allowed by their seat. Check your safety seat instructions. Most convertible safety seats have height and weight limits that will allow children to ride rear-facing for 2 years or more.
|
|
4 to 7 years old
|
Use a forward-facing car seat with a harness and tether until your child reaches the top height or weight limit allowed by the car seat maker. When they outgrow the forward-facing car seat with a harness, switch to a booster seat. This still should be in the back seat.
|
|
8 to 12 years old
|
Use a booster seat until your child is big enough to fit in a seat belt correctly. For a seat belt to fit correctly, the lap belt must be snug across the upper thighs, not the stomach. The shoulder belt should lie snugly across the shoulder and chest and not cross the neck or face. Remember: Your child should still ride in the back seat because it’s safer.
|
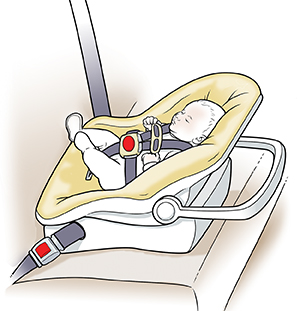
Rear-facing. Babies and toddlers should ride in rear-facing car seats as long as possible. That means until they reach the top weight or height allowed by their seat.
-
There are 2 types of rear-facing seats: infant-only and convertible. Infant-only seats must be used rear-facing. A convertible seat can be used rear-facing. But it can also be converted to forward-facing when the child reaches the height and weight set by the car seat’s maker. Most convertible safety seats have height and weight limits that will allow children to ride rear-facing for 2 years or more.
-
These seats should be reclined according to the car seat maker’s instructions. This keeps your baby’s head from flopping forward.
-
The harness should come through the car seat slots located at or below the child’s shoulders. Always follow the car seat maker’s instructions for correct harness placement.
Forward-facing. Children who have outgrown the rear-facing weight or height limit should move to a forward-facing seat with a harness. They should be in this seat up to the top weight or height allowed by the car seat.
-
Many types of seats can be used forward-facing. These include built-in seats, combination forward-facing/booster seats, and travel vests.
-
The harness should come through the car seat slots located at or above the child’s shoulders. Always follow the car seat maker’s instructions for correct harness placement.
Choosing a car seat
-
The best seat for your child is one that fits your child’s weight and height. It should also fit correctly in your car. Don’t go by price alone.
-
Try out the seat. Put your child in it and adjust the harnesses and buckles. Check that it fits your child and your car.
-
Whichever car seat you buy, check that it’s one that you'll be able to use correctly every time.
-
Buy a used car seat only if you know its crash history and its expiration date. This means that you don't buy a seat from a thrift store or online. If a car seat has been in a crash or it's past its expiration date, don't use it.
-
If you don't have the manufacturer's instructions, contact the company's service department. They'll want to know the car seat's model number, the name of the seat, and its manufacture date.
-
Follow the car seat installation instructions in your car's vehicle owner's manual
-
Check that every person who drives your child uses the correct car seat or car seat belt. This needs to occur for every trip every time. Being consistent is part of good parenting. It's safest for your child and reduces children's complaints.
Installing and using a car seat
-
Check that the seat doesn’t move more than 1 inch from side to side where the seat belt goes through the car seat (the belt path).
-
Read and follow the advice in the car seat’s manual. Keep the manual handy at all times.
-
Check your vehicle owner’s manual for information about installing car seats.
-
To check that you’ve installed your car seat correctly, contact a certified child passenger safety (CPS) technician. For more information, visit NHTSA at www.nhtsa.gov/equipment/car-seats-and-booster-seats or Safe Kids Worldwide at www.safekids.org. Your local hospital, police, or fire department may also have CPS technicians.
-
Check the car seat instructions to make sure you’re using the equipment correctly.
-
Check that harnesses are snug and flat against the child’s chest.
-
Keep the retainer clip at armpit level.
-
Always install the car seat in the back seat of the vehicle. Kids younger than age 13 should always sit in the back seat. This is safer in case of a car crash.
-
Don’t use a car seat after it's reached its expiration date. This is often when the seat is about 6 years old. Check the car seat manual for information.
-
Don't use a car seat that has any visible damage to it or that's been in a car accident. Replace the car seat after any crash.
-
Don't use a car seat that's been recalled. To check your car seat, visit NHTSA at www.nhtsa.gov/recalls .
-
Upgrade your child’s car seat as they grow. Keep track of the child’s height and weight taken at healthcare provider visits. That way you'll know if your child has outgrown their car seat.
-
When your child has outgrown a car seat, switch to a booster seat.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Amy Finke RN BSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Liora C Adler MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Stacey Wojcik MBA BSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
4/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.